Most of us don’t have the opportunity to get up close and personal to the hemp plant when it’s still growing in its natural habitat
It’s true—even the most monochrome batch of hemp flower contains what must be nature’s version of a chemical factory. Science has uncovered the presence of over 300 unique chemical compounds within the plant, many of them not found anywhere else in the plant kingdom.
Now, we can’t blame you if you thought hemp was all about CBD. We humans have a tendency towards oversimplification, at least when it seems to help us make sense of things
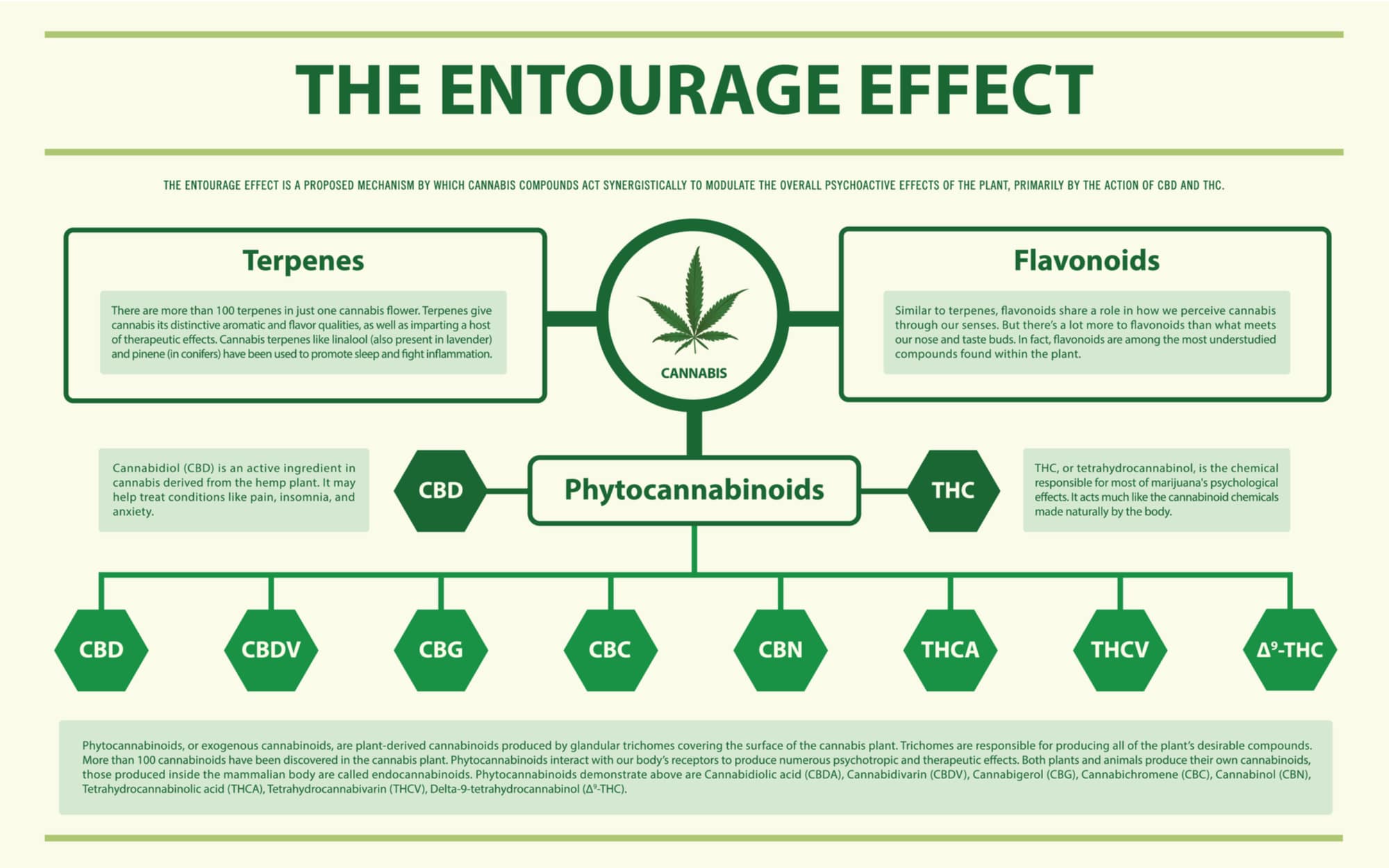
But the truth is that CBD is just the start. When taken alongside hemp’s other “active ingredients,” CBD’s power is harnessed and amplified. Scientists call this phenomenon the entourage effect—and this article will be all about it.
What is the Entourage Effect?
When you take a full spectrum CBD product, your body gets simultaneous access to hundreds of plant compounds. Some amplify CBD, and some just balance each other out. These trace compounds also help our body’s endocannabinoid receptors literally ‘open up’ and process CBD better. All of that is the entourage effect
The entourage effect can be conceptualized with an analogy. You know how your behavior changes depending on the social situation you’re in? Say you’re going to check out a new restaurant or nightclub, for example: You might feel more confident (and more excited) doing so accompanied by a significant other or even surrounded by a group of good friends than you would if you ventured out alone. CBD’s action within our body is pretty much the same way. It really shines when surrounded by others! When purified and stripped down to CBD isolate form, however, CBD loses much of its efficacy
Terpenes vs. Cannabinoids
What others, you might ask? A class of molecules called terpenes is among the most important. Terpenes have a lot in common with cannabinoids, but they also have some intriguing differences. Here’s a closer look.
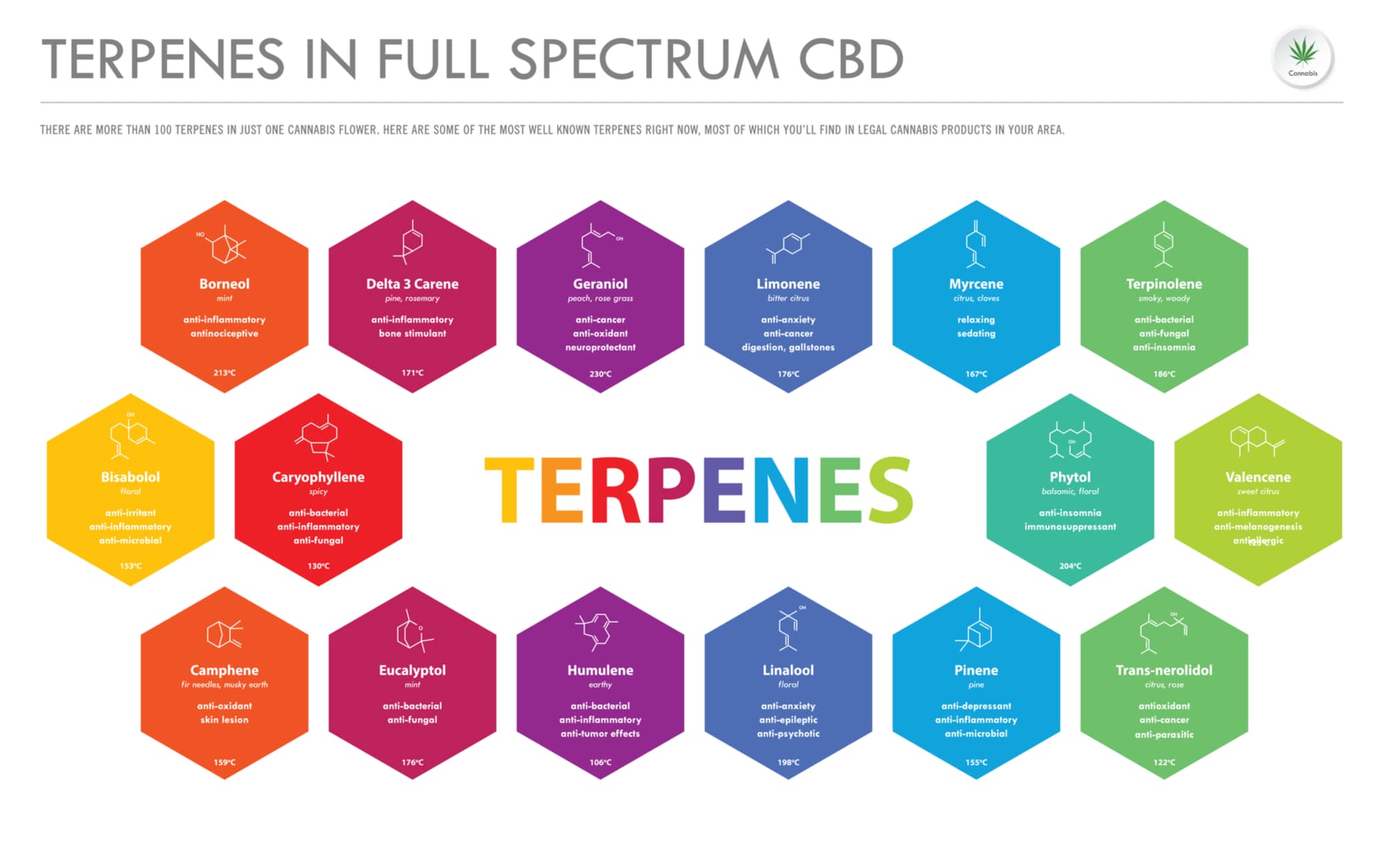
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are hemp’s ‘scent molecules.’ You can think of them almost like essential oils. Though you may not be all that familiar with terpenes, your sense of smell definitely is.
Most individual terpenes can be traced back to a certain plant or herb that contains a lot of it. Lemon essential oil, for example, gets 70% of its mass from the terpene limonene. Eucalyptus contains a terpene called eucalyptol, lavender contains linalool. The much-touted practice of ‘forest bathing’ is effective thanks in large part to the pine terpene pinene.
As you can see, terpenes are not unusual . . . but the way that hemp features so many of them most definitely is. Hemp contains dozens (maybe hundreds!) of different terpenes, many of which were once thought to be present only in their namesake plants. It turns out that’s not the case—hemp contains limonene and eucalyptol and linalool and pinene and more.
Different ‘strains’ of cannabis have different terpene profiles, which is why both high-THC cannabis and low-THC cannabis (i.e, hemp) vary in their smell and effects. Here are some of the terpenes you can expect to find in our hemp plants:
List of Terpenes
Limonene
Limonene is one of the easiest terpenes to detect. It has a potent citrus scent—and pretty potent health benefits! Able to stimulate the mind, limonene has been tied to reductions in anxiety.
It also seems to have direct benefits for health issues like inflammation and chronic pain.
Thankfully, limonene is also very bioavailable, which makes it a major contributor to the entourage effect.
β-caryophyllene
This terpene is found in black pepper, cloves, cinnamon, and cannabis. β-caryophyllene is important because it actually binds to endocannabinoid receptors—so strongly, in fact, that some researchers say it’s also a cannabinoid. Cannabis expert and botanist Ethan Russo called β-caryophyllene “the first proven phytocannabinoid” that went “beyond the cannabis [plant family].” Partially thanks to its ECS-modulating effects, β-caryophyllene is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent.
Linalool
This terpene occurs naturally within flowering plants like lavender and patchouli. Because of its lavender origin, linalool has been extensively studied. The findings? Research shows linalool can calm the central nervous system en route to promoting better health. The terpene may even reduce the damage caused by certain neurological problems.
α-pinene
As we mentioned earlier, pinene is made by pine trees and responsible for some of the benefits seen with ‘forest bathing.’ But it’s also found in basil and parsley and hemp
Think of pinene as one of nature’s nootropics: it may improve both memory and concentration. It’s an effective bronchodilator when vaporized, but it also has anti-anxiety effects.
Myrcene
Myrcene is found in mangos, basil, and the cousin of cannabis, hops. According to a 2010 analysis myrcene is the most prevalent terpene in high-THC cannabis. Most users find that myrcene reduces pain and promotes deep relaxation. Like CBD, myrcene works partially through TRPV receptors that regulate certain inflammatory pathways. When it comes to the entourage effect—the more receptor systems, the merrier!
What are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are the namesake active compounds found in cannabis. You’ve almost certainly heard of the most famous two, THC and CBD, but that’s just the start. Hemp contains dozens of other important cannabinoids, too.
List of Cannabinoids in Hemp
CBG
Cannabigerolor CBG, is one of hemp’s most important trace cannabinoids.
Why’s that? Because although it only comprises a percentage or two of mature hemp, every other cannabinoid (including CBD) is actually made from CBG. CBG is the precursor of them all—“the mother cannabinoid.”
So bonus points for those who can get their hands on fresh, ‘young’ hemp flower because that’s where CBG (and CBGa) are most concentrated.
Yet even the small amount of CBG left in fully mature hemp still offers sizable health benefits. Initial research indicates CBG may be amazing for gut health. Given that CBG is antimicrobial, anti-bacterial, and anti-inflammatory, maybe we shouldn’t be surprised.
CBN
CBG might be the very first cannabinoid to show up in hemp . . . but CBN is the very last. Short for cannabinol, CBN seems to be especially good at promoting good sleep!
CBN is fully decarboxylated (i.e, broken down by heat) and fully reduced. It’s almost like CBN is more easily ‘digested’ by the body than other cannabinoids because the environment has already been working on it.
CBN is found in ‘over ripe’ hemp—and in specialty CBD-based oils. Though unfortunately still pretty rare, customers report that CBN-infused oils really do work (especially for sleep). They can be formulated in one of two ways: either by heating ‘raw’ hemp extract for longer than normal prior to bottling, or by extracting with a CBN-rich strain of hemp.
Another interesting trait? Virtually every cannabinoid out there (including CBD and THC) breaks down to form CBN. This is reflected, if only indirectly, in the fact that large amounts of CBN are more psychotropic than CBD but less psychotropic than THC. CBN occupies what is basically a trimmed-down, simplified middle ground between the two of them.
CBC
Cannabichromene is one of the hemp’s “big six” cannabinoids, and you’ve got to admit it has a pretty cool name. It’s surprising that CBC would continue to stay under the public radar, but it has . . .
Like CBD, CBC is non-psychotropic. Unlike CBD, it has a higher affinity for pain receptors than it does for any targets within the endocannabinoid system. CBC may also reduce inflammation and boost the body’s anandamide levels, so it could be great for mood. In another study, CBC even demonstrated an ability to fight acne.
CBDa
If you think this one looks kind of familiar, you’re onto something: CBDa, or cannabidiolic acid, is the precursor of CBD.
In other words, it’s raw CBD. Just as coffee beans and potatoes and so many other ingestibles need to be heated to release their inner goodness (i.e., to make their nutrients more bioavailable), hemp extracts need to be decarbed to actually contain CBD
Many people don’t realize this distinction, but it’s there. If you walk onto a hemp farm, pick out the best-looking bud, and eat it . . . you won’t actually be getting much CBD. You’ll be getting CBDa
So, what does CBDa do? Good question! It has a larger molecular mass than CBD, so it doesn’t really pass through the blood-brain-barrier and activate endocannabinoid receptors. It’s ‘key’ doesn’t fit that ‘lock.’ Instead CBDa directly hits serotonin 5-HT1A receptors, which leads to an unexpected side effect: reduced anxiety.
CBD is already pretty great for anxiety, but its raw form is even better
According to this study, CBDa was 100 times more active than CBD at the 5-HT1A receptor—meaning it reduced anxiety more effectively, even in small amounts. Like CBD, however, CBDa has a “bell-shaped” dosing curve where its effects diminish after a certain point.
THCa
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid: it’s to THC what CBDa is to CBD. Aka, the raw form.
THCa is not psychotropic. That’s because, like CBDa, its molecular structure is a little too large and awkward to get into the brain easily
Instead THCa shines in other areas. It may be anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-proliferative, and neuroprotective . . . and that’s just for starters. THCa may also be effective against seizure disorders like epilepsy. Interested in trying THCa? It’s as easy as eating or juicing raw cannabis (if you live in an area where that’s legal, of course).
Most people don’t know this, but cannabinoids are actually a type of terpene themselves. They definitely fit the definition, which is “any of numerous hydrocarbons found especially in essential oils, resins, and balsams.” This is a perfect example of how it’s all connected!
How Cannabinoids and Terpenes Work Together
At the heart of the entourage effect’s inner workings is how cannabinoids and terpenes amplify each other. What makes this possible?
That’s a good question . . . but a tough one to answer. Many researchers suspect that the endocannabinoid system is paired with other receptor systems, allowing them to communicate in a roughly reciprocal fashion. When one system is up, the thinking goes, all systems can benefit. Scientists call this concept “cross-talk,” and it explains why a single terpene is able to increase the effect of cannabis as a whole.
Indeed, most terpenes appear to make cannabinoids stronger. Some terpenes actually change the shape of endocannabinoid receptors so CBD and other cannabinoids can bind to them more effectively. This amazing process is called conformational change.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why choose full spectrum CBD?
While the entourage effect is pretty impressive, there’s a kicker: only full spectrum CBD products harness its full power. If a CBD product is missing important cannabinoids or terpenes, then it probably won’t be as effective.
For decades this concept was just theoretical. But in 2015 a very important study from the University of Jerusalem finally brought theory to practice by comparing CBD isolate to a special CBD-rich cannabis extract. CBD isolate, for those unfamiliar, is purified CBD with no trace compounds.
The findings were fascinating. Researchers identified a “bell-shaped dose-response” associated with CBD isolate, which “limit[ed] its clinical use.” The full spectrum extract, on the other hand, “provided a clear correlation between the anti-inflammatory and anti- nociceptive responses and the dose, with increasing responses upon increasing doses.”
In other words, CBD isolate dosing can be overdone fairly easily. But full spectrum CBD? It contains enough chemical checks and balances to avoid any diminishing returns. If you want to get the best return on your investment, full spectrum CBD is the way to go.
How do I experience the entourage effect?
Experiencing the entourage effect is simple: just take full spectrum CBD oil consistently! Want to evolve a step further? You could even take CBD alongside known absorption boosters like black pepper or mango. Many of these substances work because their terpenes further amplify hemp’s entourage effect. Pretty amazing, right?
Does the entourage effect apply to CBD isolate products?
Unfortunately, no. By definition CBD isolate contains only one molecule—it’s CBD only, with no metaphorical “entourage” accompanying it. While CBD isolate doesn’t have the terpenes or trace cannabinoids needed to engage the entourage effect, it still works for some people. But why settle for good when nature has provided easy access to best?
By the way, the entourage effect also prohibits isolated THC use. Many people learned that the hard way when a THC-based drug called Marinol came out in the 80s. It had all sorts of unpleasant side effects and lacked the relaxing feelings associated with whole-plant cannabis. Research continues to be clear: the combo of CBD and THC is better than THC on its own.
What does the entourage effect mean for CBD?
The entourage effect places CBD in its rightful place. It’s not everything, and it’s not a panacea . . . but it is a critical part of hemp’s infrastructure that’s needed to experience the plant’s best.
The entourage effect also means good things for CBD research. It’s kept leading scientists busy for a few decades so far! In the future, it’s likely that new and novel cannabinoid + terpene combos with specialized effects will be unearthed. Maybe a certain blend of CBD, CBN, and linalool will prove effective for certain ailments, or maybe hemp will be bred to contain CBC, not just CBD. Who knows?
How many mg of CBD will make you feel the entourage effect?
More research is needed to definitively answer that one, but we can provide some pointers. It’s likely that 5-10 milligrams of full spectrum CBD taken twice daily is a good baseline dosage. Though this type of dose only contains trace amounts of other cannabinoids and terpenes, their synergistic power is more than enough to harness the entourage effect and have you feeling your best
What does the entourage effect feel like?
Speaking of feelings, those associated with the entourage effect are among CBD’s most beloved. When one really gets their dosing right, full spectrum CBD can even feel subtly euphoric. So much for the myth that CBD is nonpsychoactive.
In reality, full spectrum CBD is non-psychotropic and non-intoxicating but very much active within the mind. That’s the power of hemp’s 300+ active ingredients all synergizing and actively working together for you.
To Your Health
Green Maiden